| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
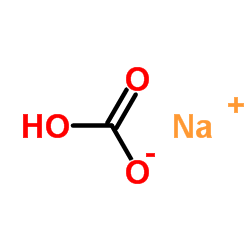 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
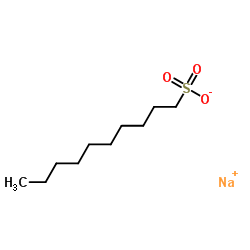 |
sodium decylsulfonate
CAS:13419-61-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
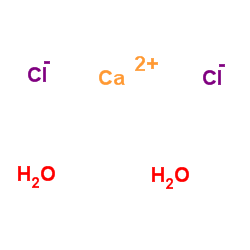 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |