| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Lithium diisopropylamide
CAS:4111-54-0 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Dexamethasone
CAS:50-02-2 |
|
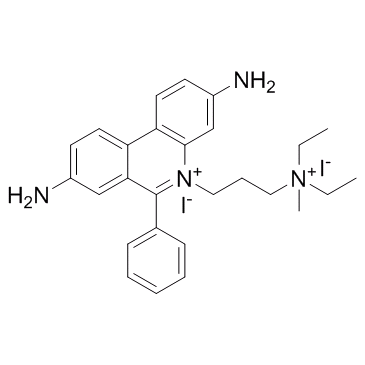 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
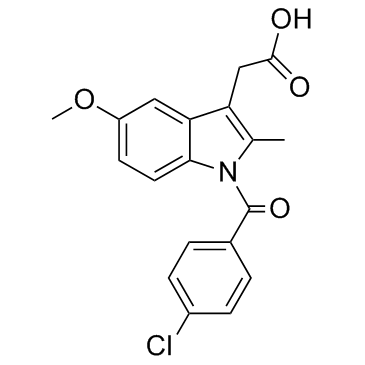 |
Indometacin
CAS:53-86-1 |
|
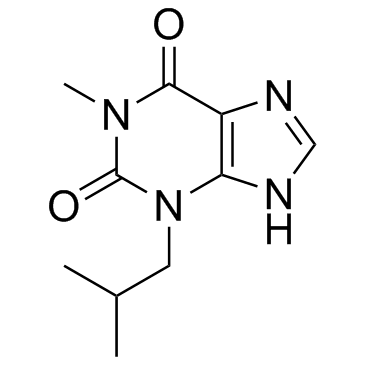 |
3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine
CAS:28822-58-4 |