| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
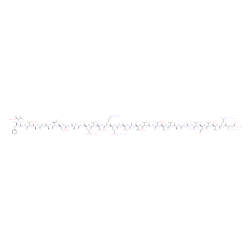 |
α-Synuclein (61-95) (human) trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:154040-19-4 |
|
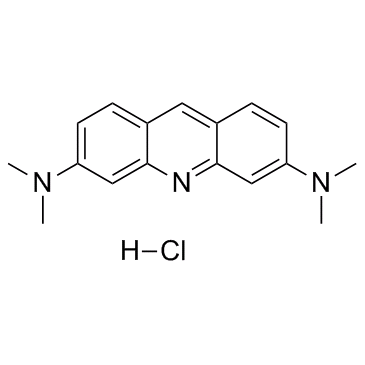 |
Acridine Orange hydrochloride
CAS:65-61-2 |
|
 |
Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
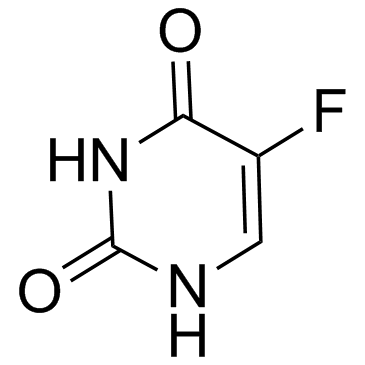 |
Fluorouracil
CAS:51-21-8 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
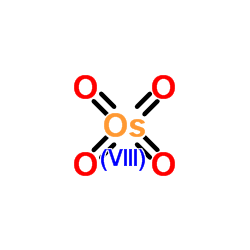 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
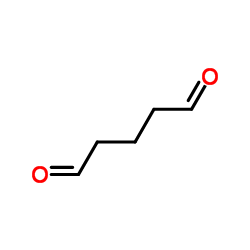 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
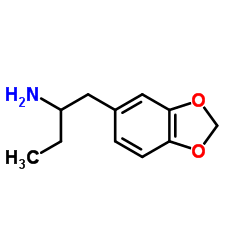 |
1,3-Benzodioxolylbutanamine
CAS:42542-07-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |