| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
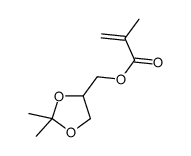 |
(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methyl methacrylate
CAS:7098-80-8 |
|
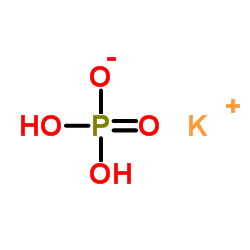 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
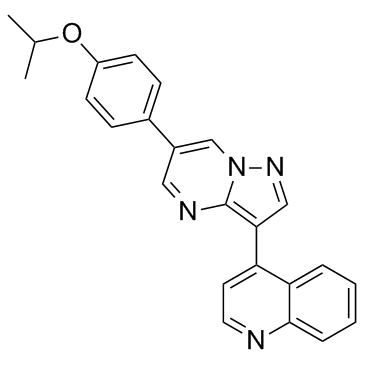 |
DMH-1
CAS:1206711-16-1 |