| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
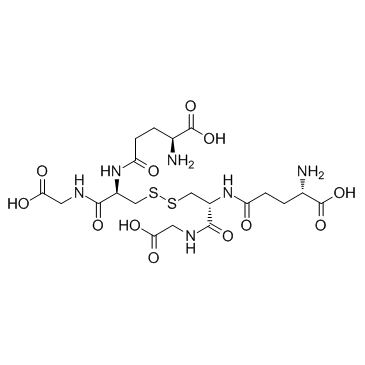 |
L(-)-Glutathione
CAS:27025-41-8 |
|
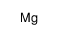 |
Magnesium
CAS:7439-95-4 |
|
 |
Zinc
CAS:7440-66-6 |
|
 |
Calcium
CAS:7440-70-2 |
|
 |
Strontium
CAS:7440-24-6 |
|
 |
L-cysteine
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
 |
Aluminum Powder
CAS:7429-90-5 |
|
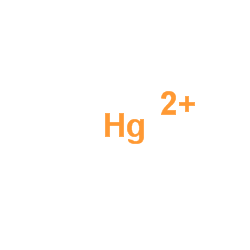 |
mercury(II) cation
CAS:7439-97-6 |
|
 |
tin
CAS:7440-31-5 |
|
 |
chromium
CAS:7440-47-3 |