| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Manganese chloride
CAS:7773-01-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium Nitrate Hexahydrate
CAS:13446-18-9 |
|
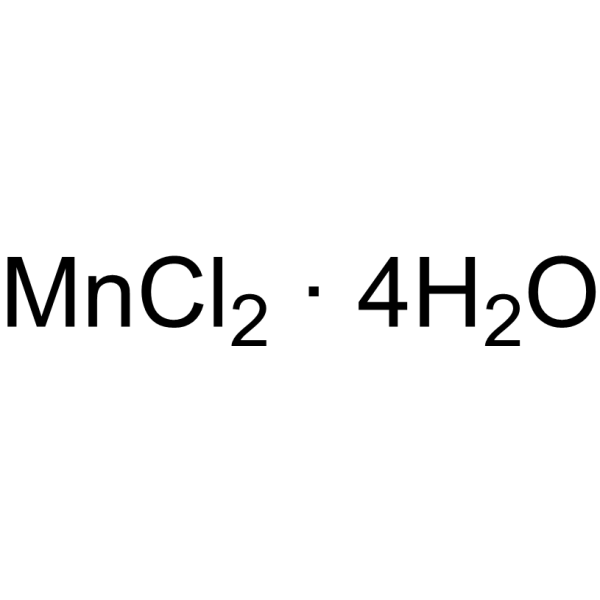 |
Manganese chloride tetrahydrate
CAS:13446-34-9 |