| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
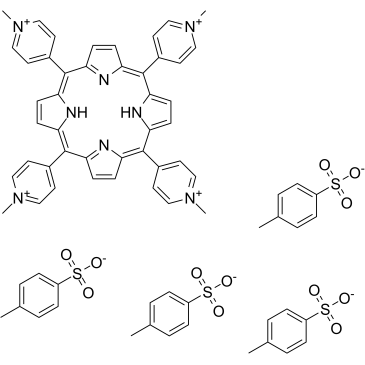 |
5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphine tetratosylate
CAS:36951-72-1 |
|
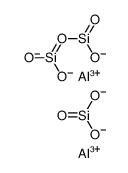 |
Aluminatesilicate
CAS:1327-36-2 |