| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
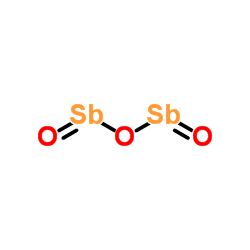 |
Diantimony trioxide
CAS:1309-64-4 |
|
 |
Antimony
CAS:7440-36-0 |