| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
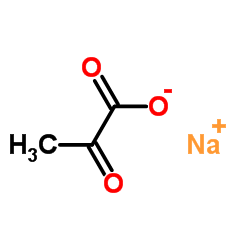 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
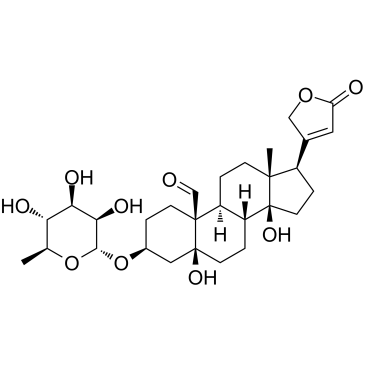 |
CONVALLATOXIN
CAS:508-75-8 |
|
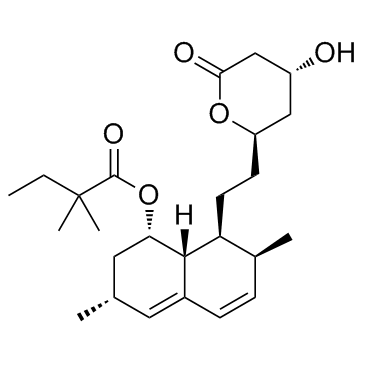 |
Simvastatin
CAS:79902-63-9 |
|
 |
Dexamethasone
CAS:50-02-2 |
|
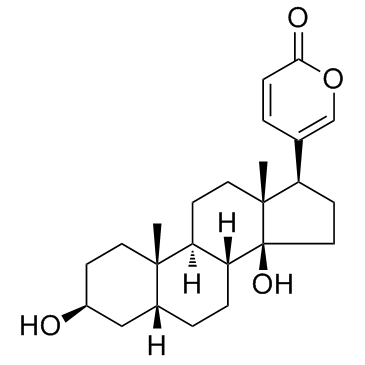 |
Bufalin
CAS:465-21-4 |