| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
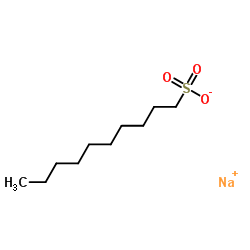 |
sodium decylsulfonate
CAS:13419-61-9 |
|
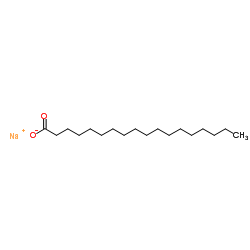 |
Sodium stearate
CAS:822-16-2 |
|
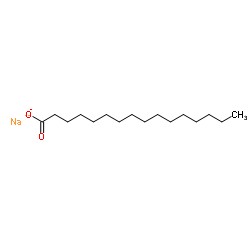 |
Palmitic acid sodium
CAS:408-35-5 |