| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
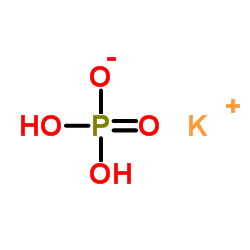 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
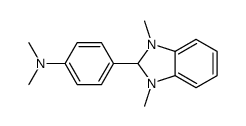 |
1,3-Dimethyl-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzoimidazole
CAS:302818-73-1 |