| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
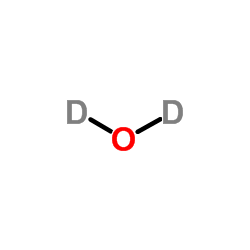 |
Heavy water
CAS:7789-20-0 |
|
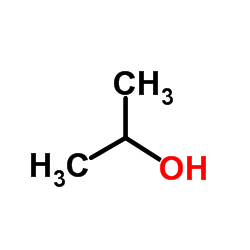 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
DL-Serine
CAS:302-84-1 |
|
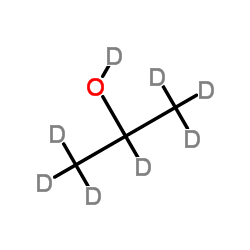 |
2-(2H7)Propan(2H)ol
CAS:22739-76-0 |
|
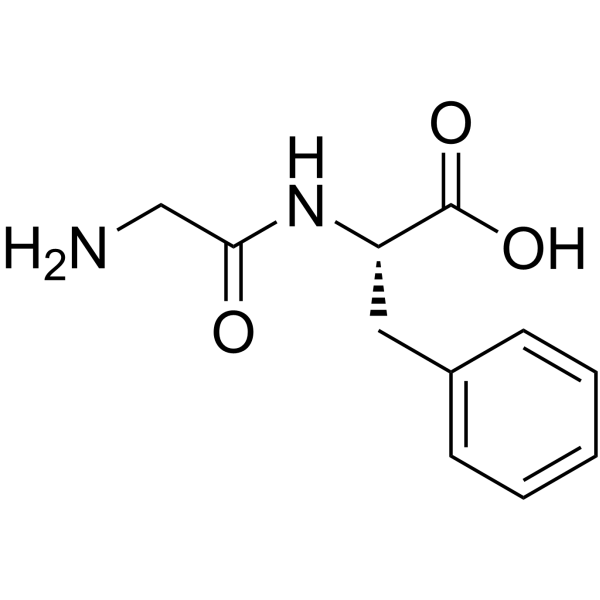 |
H-Gly-Phe-OH
CAS:3321-03-7 |