AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses
1990-07-01
Reversal of azidothymidine-induced bone marrow suppression by 2',3'-dideoxythymidine as studied by hemopoietic clonal culture.
Y Yoshida, C Yoshida
Index: AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 6(7) , 929-32, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The hematological toxicity of the antiviral drug azidothymidine (AZT) was studied in vitro by measuring the cell growth of hematopoietic progenitor cells obtained from normal bone marrow. AZT inhibited the growth of granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) and early and late erythroid (BFU-E and CFU-E) progenitors in a dose-dependent manner. The hemopoietic inhibition of AZT was significantly reduced by the addition of 2',3'-dideoxythymidine (2',3'-ddT). The results suggest that 2',3'-ddT may be of potential value in reducing AZT toxicity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
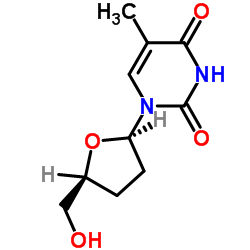 |
2',3'-Dideoxythymidine
CAS:3416-05-5 |
C10H14N2O4 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Nicotinamide exacerbates hypoxemia in ventilator-induced lun...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0123460, (2015)] |
|
Metabolic drug-drug interaction potential of macrolactin A a...
2014-09-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(9) , 5036-46, (2014)] |
|
Cuboplexes: Topologically Active siRNA Delivery.
2015-10-27 [ACS Nano 9 , 10214-26, (2015)] |
|
Synergistic inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type ...
1991-10-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35(10) , 2003-11, (1991)] |
|
Permeation and salvage of dideoxyadenosine in mammalian cell...
1989-07-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 36(1) , 185-92, (1989)] |