| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
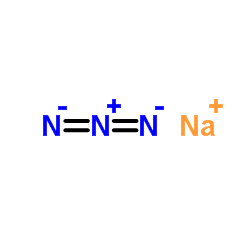 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
Germanium
CAS:7440-56-4 |
|
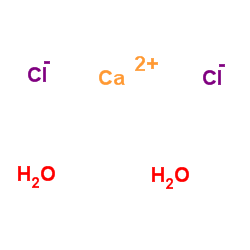 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
trisodium phosphate
CAS:7601-54-9 |
|
 |
Native Aspergillus niger Amyloglucosidase
CAS:9032-08-0 |