| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
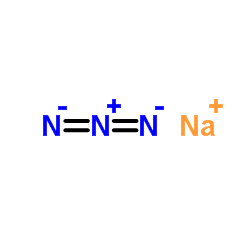 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
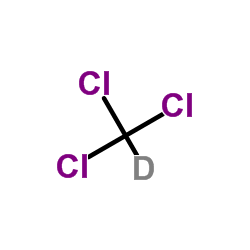 |
chloroform-d
CAS:865-49-6 |
|
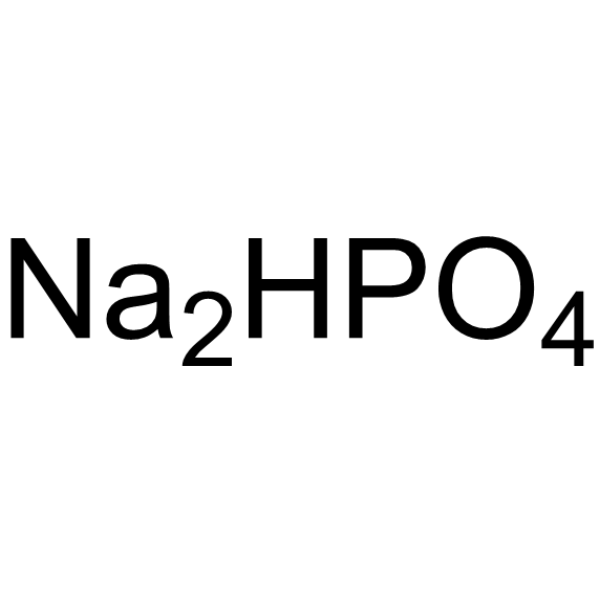 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
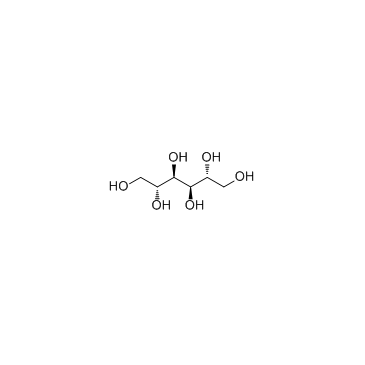 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
 |
H-Ser(Bzl)-OH
CAS:4726-96-9 |