| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
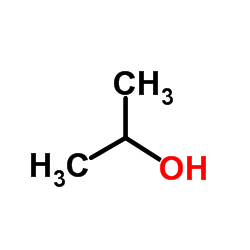 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
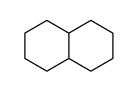 |
Decahydronaphthalene
CAS:91-17-8 |
|
 |
cyclohexane
CAS:110-82-7 |
|
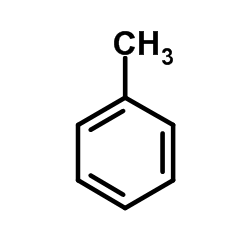 |
Toluene
CAS:108-88-3 |