| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
bisphenol A
CAS:80-05-7 |
|
 |
titanium dioxide
CAS:13463-67-7 |
|
 |
Titanium oxide
CAS:1317-80-2 |
|
 |
Copper
CAS:7440-50-8 |
|
 |
Cupric oxide
CAS:1317-38-0 |
|
 |
Titanium(IV) oxide, anatase
CAS:1317-70-0 |
|
 |
titanium
CAS:7440-32-6 |
|
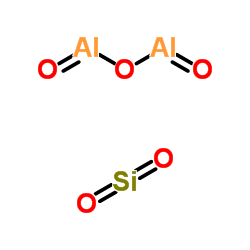 |
Zeolite
CAS:1318-02-1 |