| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
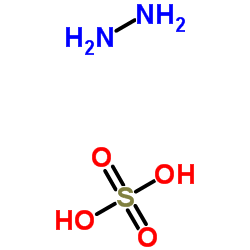 |
Hydrazine sulfate
CAS:10034-93-2 |
|
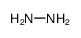 |
HYDRAZINE
CAS:302-01-2 |
|
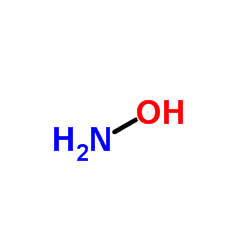 |
Hydroxylamine
CAS:7803-49-8 |
|
 |
Hydrazine hemisulfate salt
CAS:13464-80-7 |
|
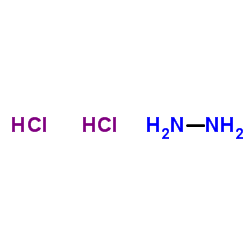 |
Hydrazine Dihydrochloride
CAS:5341-61-7 |