| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
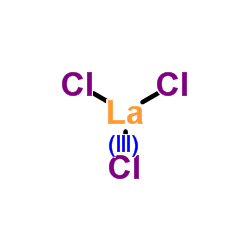 |
Lanthanum(III) chloride
CAS:10099-58-8 |
|
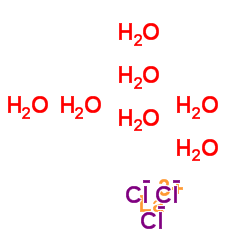 |
lanthanum chloride heptahydrate
CAS:10025-84-0 |
|
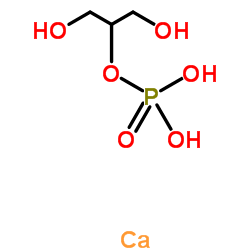 |
calcium 1,3-hydroxypropyl phosphate
CAS:58409-70-4 |