| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
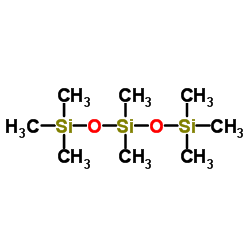 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
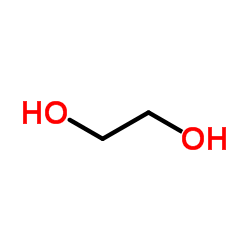 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
 |
4-Nonylphenol branched ethoxylated
CAS:127087-87-0 |