| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
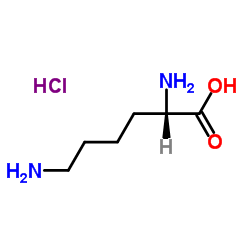 |
L-Lysine hydrochloride
CAS:10098-89-2 |
|
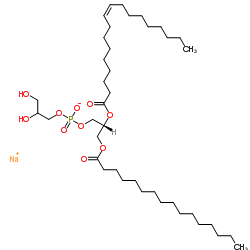 |
1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol) (sodium salt)
CAS:268550-95-4 |