| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
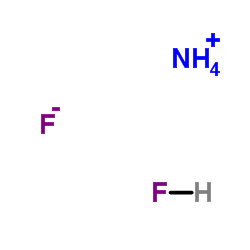 |
Ammonium bifluoride
CAS:1341-49-7 |
|
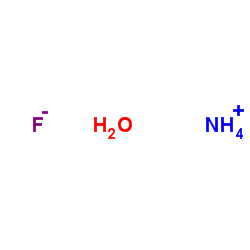 |
Ammonium fluoride
CAS:12125-01-8 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
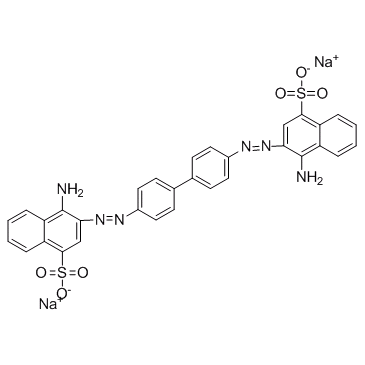 |
Congo Red
CAS:573-58-0 |