| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
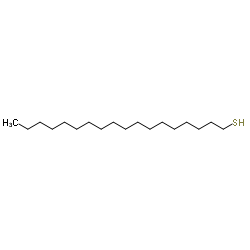 |
octadecylthiol
CAS:2885-00-9 |
|
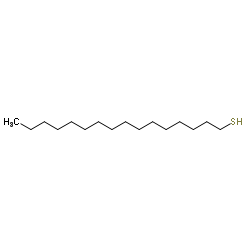 |
Cetylmercaptan
CAS:2917-26-2 |
|
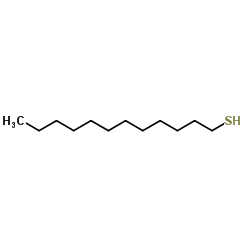 |
1-Dodecanethiol
CAS:112-55-0 |