| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
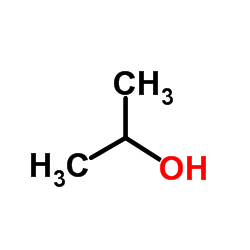 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
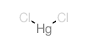 |
Mercury chloride
CAS:7487-94-7 |
|
 |
Cupric chloride
CAS:7447-39-4 |
|
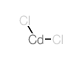 |
Cadmium chloride
CAS:10108-64-2 |
|
 |
Mercury(I) chloride
CAS:10112-91-1 |