| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
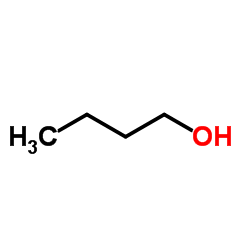 |
Butanol
CAS:71-36-3 |
|
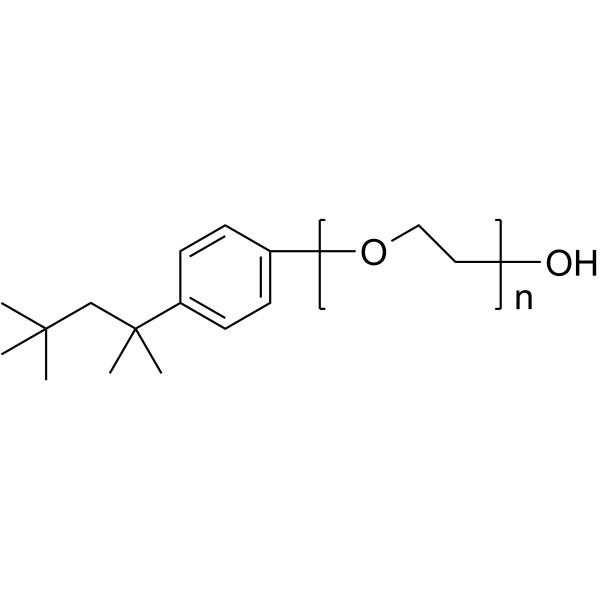 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
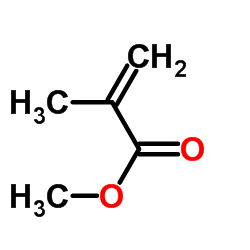 |
Methyl methacrylate
CAS:80-62-6 |
|
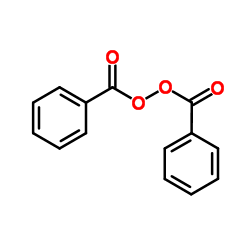 |
Benzoyl peroxide
CAS:94-36-0 |
|
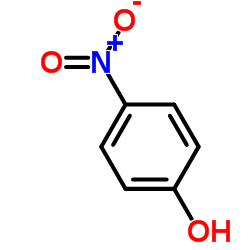 |
4-Nitrophenol
CAS:100-02-7 |