| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
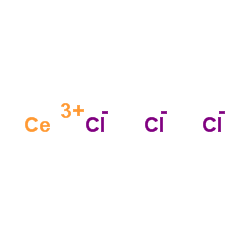 |
cerium(iii) chloride
CAS:7790-86-5 |
|
 |
Cerium(III) Chloride Heptahydrate
CAS:18618-55-8 |