| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
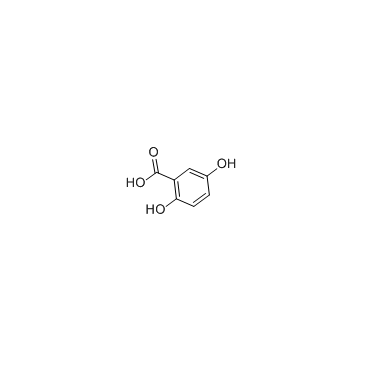 |
Gentisic acid
CAS:490-79-9 |
|
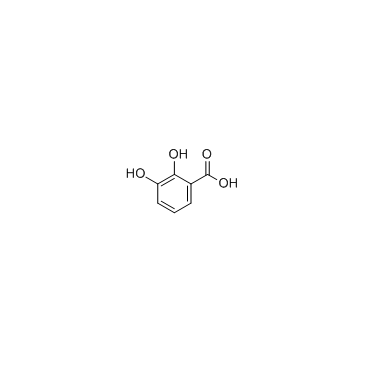 |
2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:303-38-8 |