| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
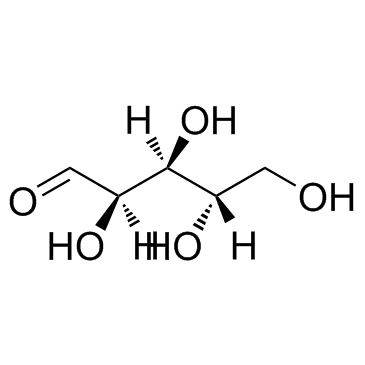 |
L-(+)-Arabinose
CAS:5328-37-0 |
|
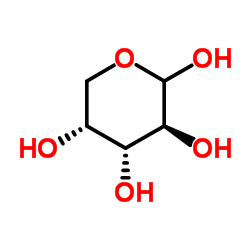 |
D-Arabinose
CAS:10323-20-3 |
|
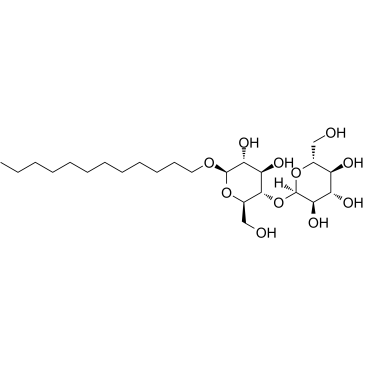 |
n-Dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside
CAS:69227-93-6 |
|
 |
Restriction Endonuclease
CAS:84628-87-5 |