| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
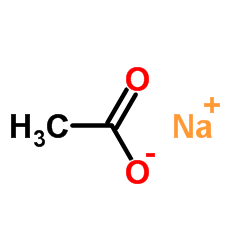 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
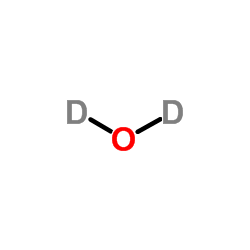 |
Heavy water
CAS:7789-20-0 |
|
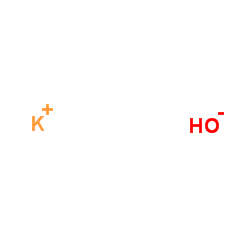 |
Potassium hydroxide
CAS:1310-58-3 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
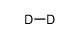 |
deuterium
CAS:7782-39-0 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
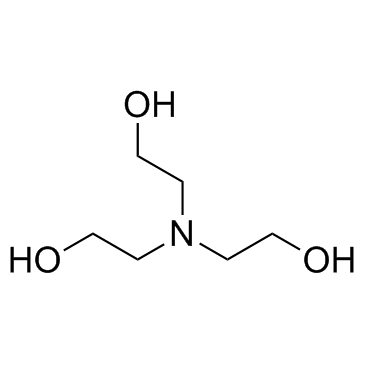 |
Triethanolamine
CAS:102-71-6 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
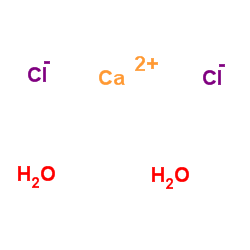 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |