| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
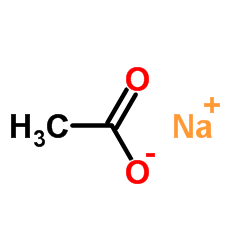 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
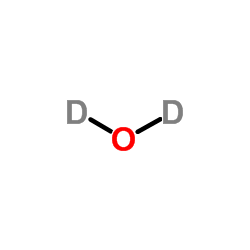 |
Heavy water
CAS:7789-20-0 |
|
 |
HYDROFLUORIC ACID
CAS:7664-39-3 |
|
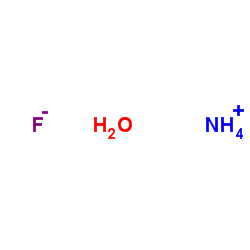 |
Ammonium fluoride
CAS:12125-01-8 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
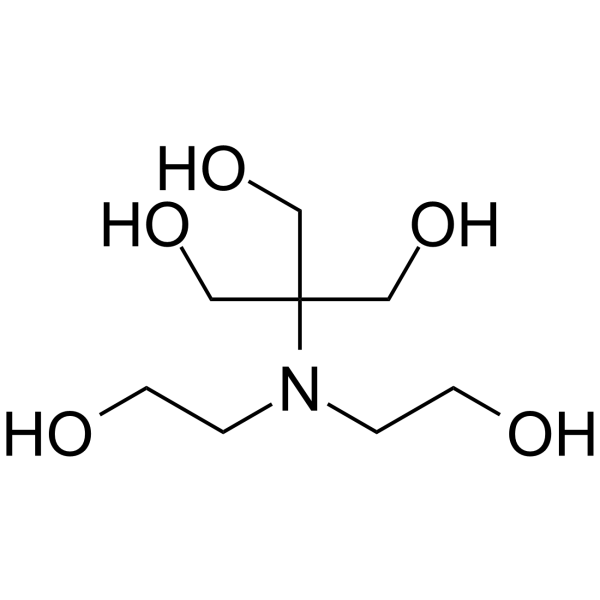 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
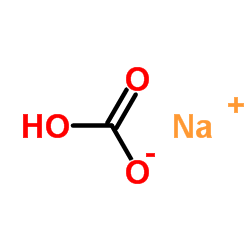 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
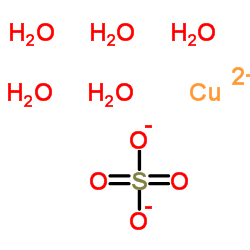 |
Cupric sulfate
CAS:7758-98-7 |
|
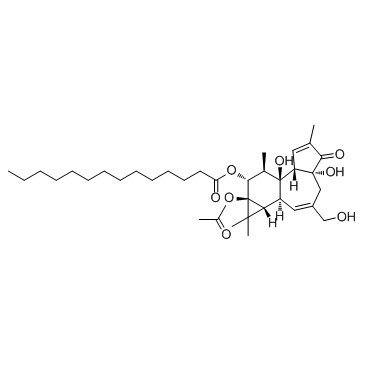 |
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
CAS:16561-29-8 |
|
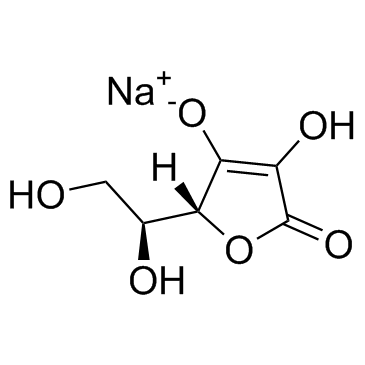 |
sodium ascorbate
CAS:134-03-2 |