| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
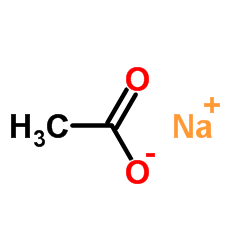 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
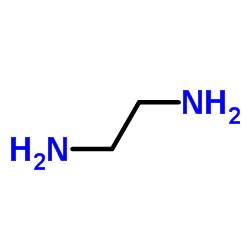 |
1,2-Ethanediamine
CAS:107-15-3 |
|
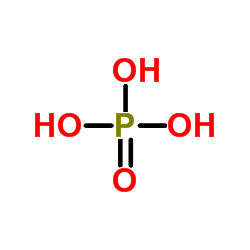 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
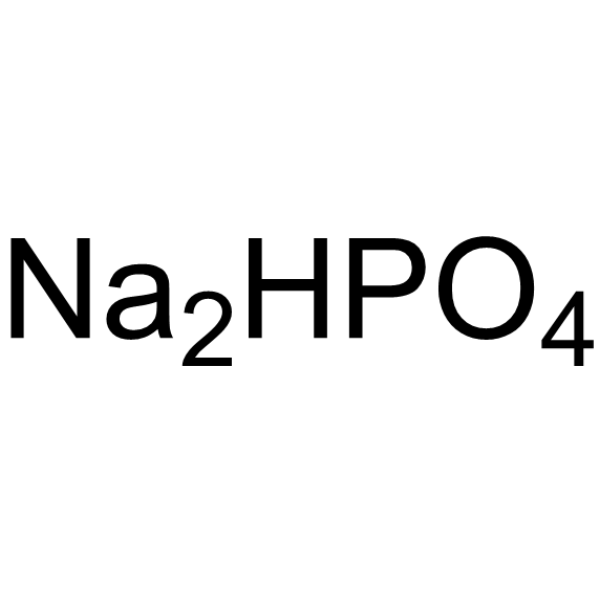 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
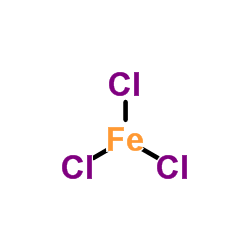 |
Ferric chloride
CAS:7705-08-0 |