| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
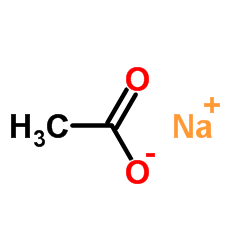 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
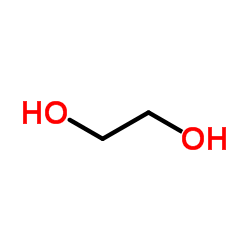 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
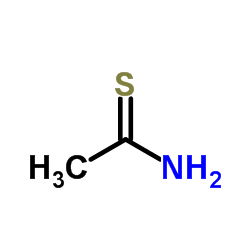 |
Thioacetamide
CAS:62-55-5 |