| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
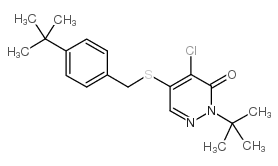 |
Pyridaben
CAS:96489-71-3 |
|
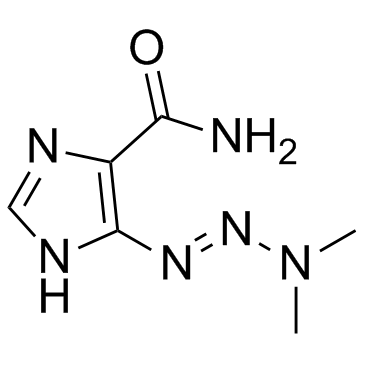 |
Dacarbazine
CAS:4342-03-4 |