| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
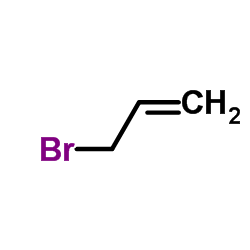 |
allyl bromide
CAS:106-95-6 |
|
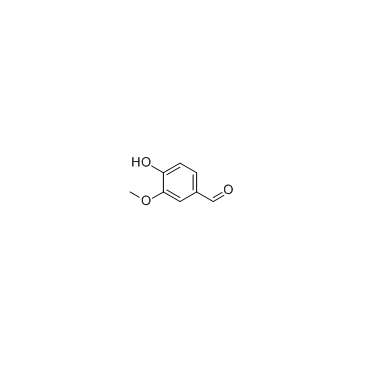 |
Vanillin
CAS:121-33-5 |
|
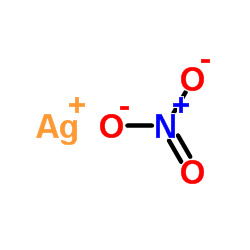 |
Silver nitrate
CAS:7761-88-8 |
|
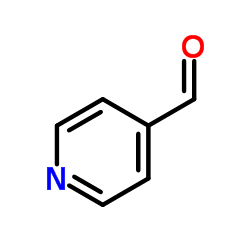 |
p-Formylpyridine
CAS:872-85-5 |
|
 |
Mitomycin C
CAS:50-07-7 |
|
 |
Heptafluorobutyric acid
CAS:375-22-4 |
|
 |
Pyrrole
CAS:109-97-7 |
|
 |
Direct Blue 14
CAS:72-57-1 |