| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
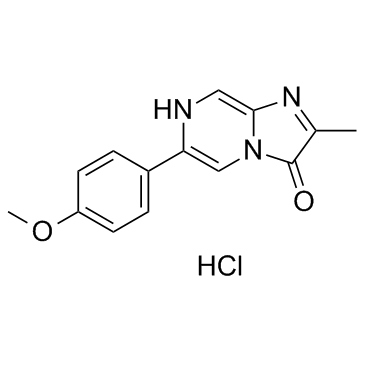 |
MCLA hydrochloride
CAS:128322-44-1 |
|
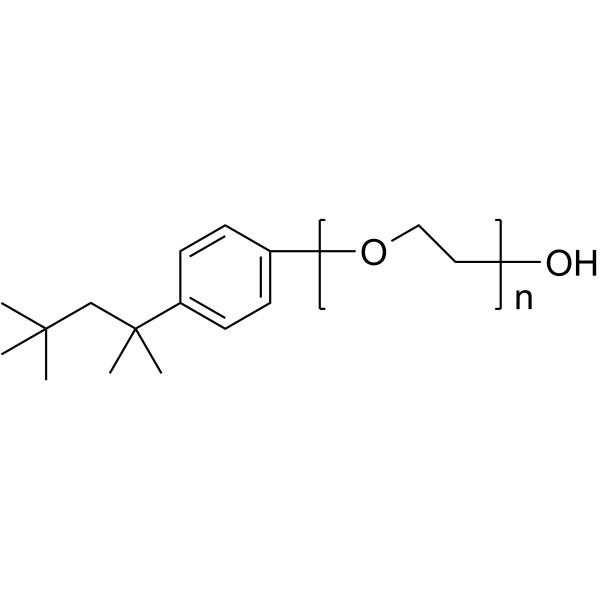 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
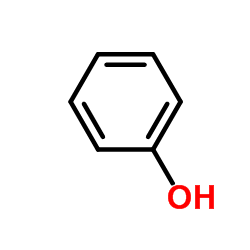 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
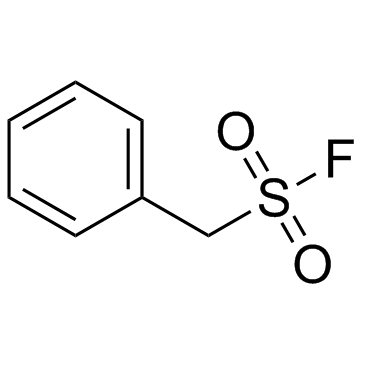 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
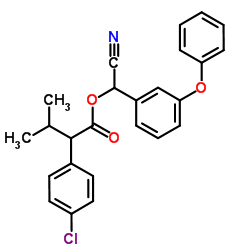 |
fenvalerate
CAS:51630-58-1 |