| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
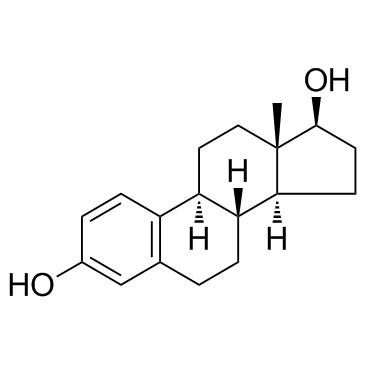 |
beta-Estradiol
CAS:50-28-2 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
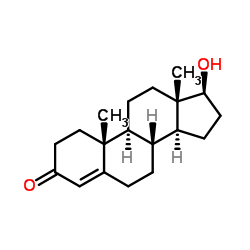 |
Testosterone
CAS:58-22-0 |