| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
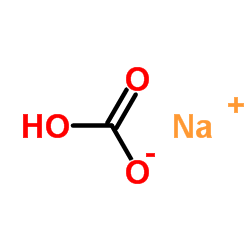 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |