| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
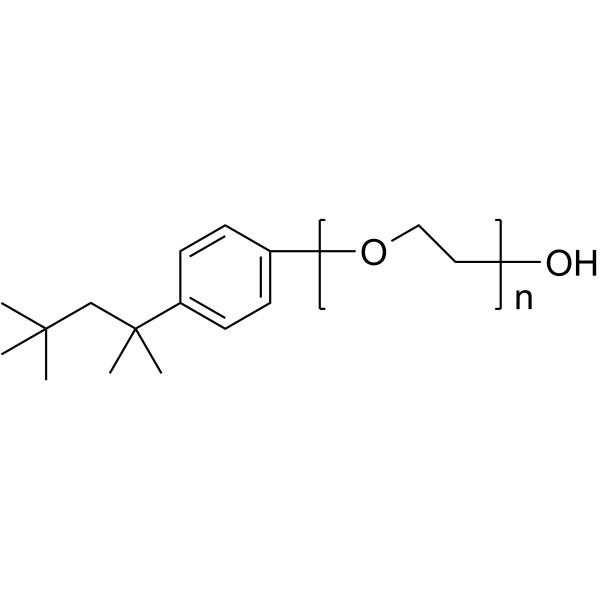 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
 |
3-Methyladenine
CAS:5142-23-4 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |