| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
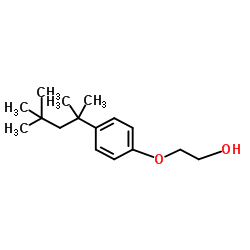 |
2-(4-(1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy)ethanol
CAS:2315-67-5 |
|
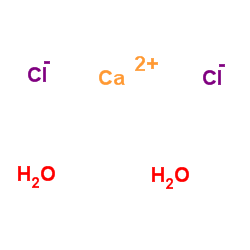 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
Maltose
CAS:69-79-4 |