| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Forskolin
CAS:66575-29-9 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
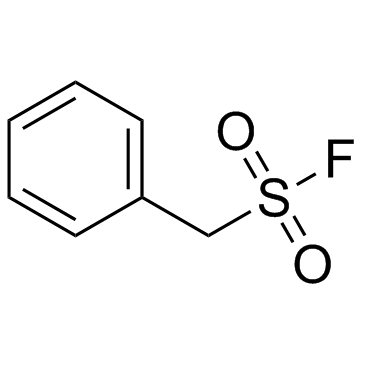 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
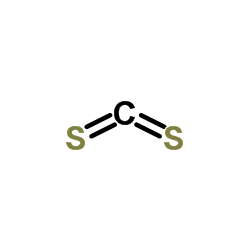 |
Carbon disulphide
CAS:75-15-0 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |