| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
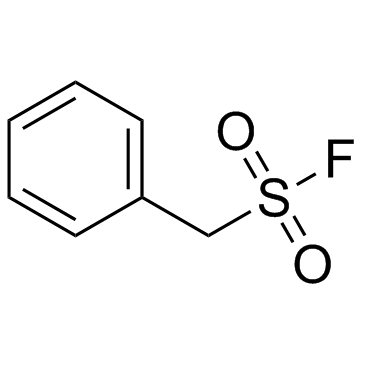 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
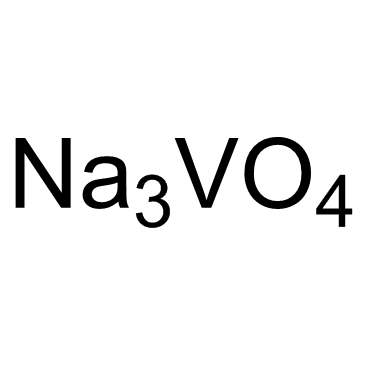 |
Sodium orthovanadate
CAS:13721-39-6 |
|
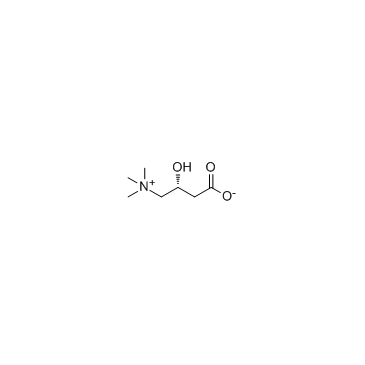 |
L-Carnitine inner salt
CAS:541-15-1 |
|
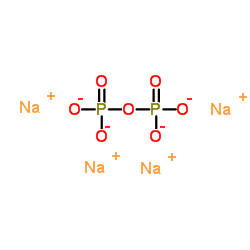 |
Tetrasodium pyrophosphate
CAS:7722-88-5 |