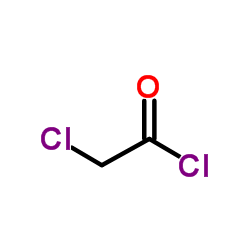
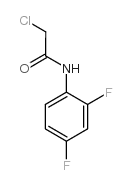
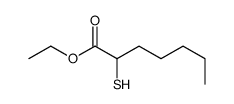
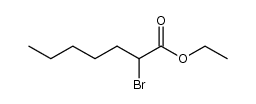
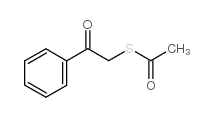
|
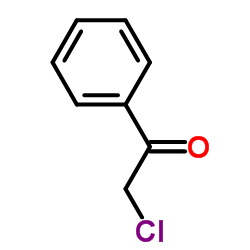
~74% |
|
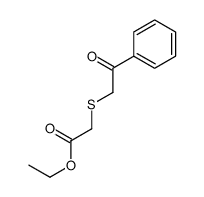
~% |
|
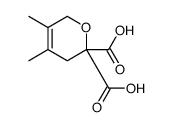
~99% |
|
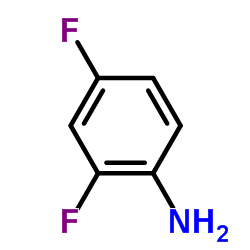
~87% |
|
~% |
|
~97% |