Potentiometric sensors arrays based on perfluorinated membranes and silica nanoparticles with surface modified by proton-acceptor groups, for the determination of aspartic and glutamic amino acids anions and potassium cations
Ekaterina Safronova, Anna Parshina, Tatyana Kоlganova, Olga Bobreshova, Gerald Pourcelly, Andrey Yaroslavtsev
Index: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.03.028
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
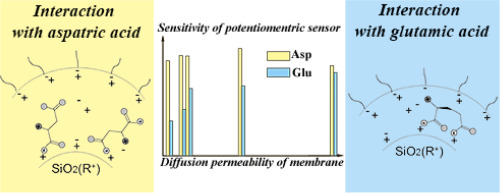
Hybrid materials based on perfluorosulfonic cation-exchange membranes and silica nanoparticles with surface modified by nitrogen-containing groups have been obtained. The influence of concentration, size and proton acceptor ability of modifying groups on the oxide surface onto the response stability and sensitivity of potentiomentric sensors in aspartic and glutamic acid solutions with pH 4–9 has been investigated. A correlation between sensor cross-sensitivity to cations and anions in test solutions and membrane diffusion permeability is revealed. Optimal membrane compositions for arrays of cross-sensitive sensors have been chosen. Proposed sensors allow to carry out a simultaneous determination of potassium cations and amino acid anions in test solutions with concentrations ranged from 1.0·10−4 to 1.0·10−2 M, with an error < 14%.
|
Mechanism studies of hydrazine electro-oxidation by a platin...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.012] |
|
Conditions for a nearly perfect match between pulse voltamme...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.004] |
|
Square wave voltammetric quantitative determination of flavo...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.009] |
|
Electrochemical characterizations and reverse electrodialysi...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.005] |
|
Mesoporous spinel manganese zinc ferrite for high-performanc...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.002] |