Detection of Adrenaline in Blood Plasma as Biomarker for Adrenal Venous Sampling
Denise Molinnus; Gabriel Hardt; Petra Siegert; Holger S. Willenberg; Arshak Poghossian; Michael Keusgen; Michael J. Schöning
Index: 10.1002/elan.201800026
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
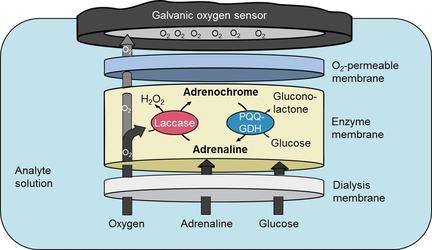
An amperometric bi‐enzyme biosensor based on substrate recycling principle for the amplification of the sensor signal has been developed for the detection of adrenaline in blood. Adrenaline can be used as biomarker verifying successful adrenal venous sampling procedure. The adrenaline biosensor has been realized via modification of a galvanic oxygen sensor with a bi‐enzyme membrane combining a genetically modified laccase and a pyrroloquinoline quinone‐dependent glucose dehydrogenase. The measurement conditions such as pH value and temperature were optimized to enhance the sensor performance. A high sensitivity and a low detection limit of about 0.5–1 nM adrenaline have been achieved in phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, relevant for measurements in blood samples. The sensitivity of the biosensor to other catecholamines such as noradrenaline, dopamine and dobutamine has been studied. Finally, the sensor has been successfully applied for the detection of adrenaline in human blood plasma.
|
Novel Green Potentiometric Method for the Determination of L...
2018-03-30 [10.1002/elan.201800132] |
|
Detection of Rocuronium in Whole Blood Using a Lipid‐Bonded ...
2018-03-15 [10.1002/elan.201800102] |
|
High Loading Pt Core/Carbon Shell Derived from Platinum‐Anil...
2018-03-15 [10.1002/elan.201800036] |
|
Non‐Covalent Functionalization of Multi‐Wall Carbon Nanotube...
2018-03-15 [10.1002/elan.201800034] |
|
Voltammetric Determination of Serine using L‐cysteine Modifi...
2018-03-15 [10.1002/elan.201700682] |