pH-responsive alginate-based hydrogels for protein delivery
Diego S. Lima, Ernandes T. Tenório-Neto, Michele K. Lima-Tenório, Marcos R. Guilherme, Débora B. Scariot, Celso V. Nakamura, Edvani C. Muniz, Adley F. Rubira
Index: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.002
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
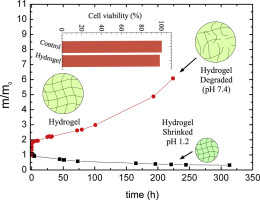
This work describes the synthesis and characterization of pH-responsive hydrogels based on alginate for protein delivery. Synthesis approach shown here has included the modification of sodium alginate to convert it into a covalently crosslinkable polysaccharide and the subsequent radical polymerization reaction with sodium acrylate and N-vinylpyrrolidone for hydrogelation. To evaluate the applicability of the obtained hydrogels as an oral protein delivery system, we studied the cytotoxicity, the drug release profile (using BSA as a protein model), and the swelling performance in the basic and acidic environments. The hydrogels showed a pH-dependent swelling profile with higher value at pH 7.4. The protein release mechanism was demonstrated to be dependent on pH and composition. The proposed materials were shown to be compatible with living cells, indicating great pharmacological potential. These results show that the hydrogels are ideally suited for use as an oral drug delivery device.
|
A viscosity model for ionic liquids based on the Eyring's th...
2018-04-11 [10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.048] |
|
Removal of diethyl phthalate via adsorption on mineral rich ...
2018-04-11 [10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.031] |
|
Study of chemical physics on energy transfer phenomenon betw...
2018-04-10 [10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.035] |
|
Carbon quantum dots-modified ferrofluid for dispersive solid...
2018-04-09 [10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.036] |
|
Piperine derivatives as green corrosion inhibitors on iron s...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.127] |