Eumelanin–Fe3O4 hybrid nanoparticles for enhanced MR/PA imaging-assisted local photothermolysis
Junqing Wang, Heng Liu, Yu Liu, Chengchao Chu, Youyuan Yang, Yun Zeng, Weiguo Zhang, Gang Liu
Index: 10.1039/C8BM00003D
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
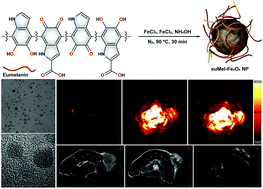
In this work, we report on biodegradable eumelanin–Fe3O4 hybrid nanoparticles (euMel–Fe3O4 NPs) for multiple imaging-assisted local photothermolysis. The euMel–Fe3O4 NPs are rationally prepared via a facile one-step co-precipitation method in the aqueous phase in the presence of eumelanin. The obtained NPs exhibited high stability and aqueous dispersity. euMel–Fe3O4 NPs could provide T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) and photoacoustic (PA) imaging contrast enhancement prior to the treatment, due to their high r2 relaxivity that was determined to be 245.88 mM−1 s−1 (a value higher than those for other commercially available iron oxide NPs) and good PA signal intensity. Besides, with effective NIR absorbance, the euMel–Fe3O4 NPs promoted an effective photothermolysis treatment in an experimental mouse model of cancer. Cytotoxicity and in vivo histological examination demonstrated no appreciable toxicity. Our work suggests that euMel–Fe3O4 NPs could be proposed as a potential class of theranostic nanoplatform with multiple imaging modalities for cancer therapy.
|
Role of Sox9 in Collagen Hydrogel-Mediated Chondrogenic Diff...
2018-04-11 [10.1039/C8BM00317C] |
|
Designing well-defined photopolymerized synthetic matrices f...
2018-04-10 [10.1039/C8BM00099A] |
|
Injectable self-assembled peptide hydrogels for glucose-medi...
2018-04-06 [10.1039/C8BM00006A] |
|
Polytyrosine nanoparticles enable ultra-high loading of doxo...
2018-04-06 [10.1039/C8BM00243F] |
|
Maintenance of the spheroid organization and properties of g...
2018-04-05 [10.1039/C7BM00559H] |