DFT-Supported Threshold Ionization Study of Chromium Biphenyl Complexes: Unveiling the Mechanisms of Substituent Influence on Redox Properties of Sandwich Compounds
Sergey Yu. Ketkov, Sheng-Yuan Tzeng, Pei-Ying Wu, Gennady V. Markin, Wen-Bih Tzeng
Index: 10.1002/chem.201702226
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
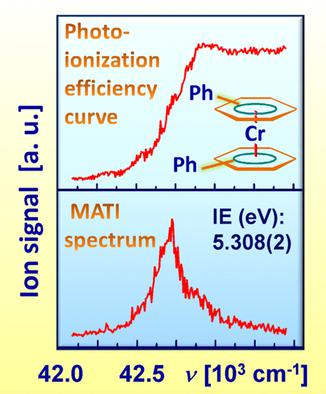
High-resolution mass-analyzed threshold ionization (MATI) spectra of (η6-Ph2)2Cr and (η6-Ph2)(η6-PhMe)Cr demonstrate that the Ph groups work as electron donors, decreasing the ionization energy of the gas-phase bisarene complexes. In contrast to electrochemical data, a close similarity of the Ph and Me group effects on the oxidation of free sandwich molecules has been revealed. However, DFT calculations testify for the opposite shifts of the electron density caused by the Me and Ph substituents in the neutral complexes, the latter behaving as an electron-accepting fragment. On the contrary, in the bisarene cations, the Ph group becomes a stronger donor than methyl. This change provides the similar substituent effects observed with the MATI experiment. On the other hand, the well-documented opposite influence of the Me and Ph fragments on the redox potential of the (η6-arene)2Cr+/0 couple in solution appears to be a result of solvation effects but not intramolecular interactions as shown for the first time in this work.
|
Subnaphthalocyanines as Electron Acceptors in Polymer Solar ...
2018-04-10 [10.1002/chem.201800596] |
|
Formal Lossen Rearrangement/[3+2] Annulation Cascade Catalyz...
2018-04-10 [10.1002/chem.201801125] |
|
A Highly Sensitive Fluorogenic Probe for Imaging Glycoprotei...
2018-04-10 [10.1002/chem.201800790] |
|
Improvement of Photodynamic Activity of Lipid–Membrane‐Incor...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/chem.201800674] |
|
Ordered Mesoporous Titania/Carbon Hybrid Monoliths for Lithi...
2018-04-06 [10.1002/chem.201801099] |