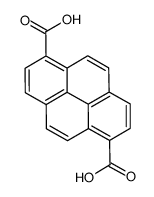
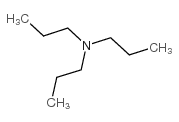
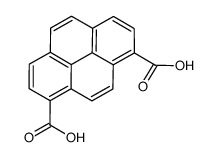
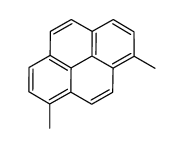
|
~97% |
|
~61% |
|
~53% |
|
~85% |