Astaxanthin-based polymers as new antimicrobial compounds
S. Weintraub, T. Shpigel, L. G. Harris, R. Schuster, E. C. Lewis, D. Y. Lewitus
Index: 10.1039/C7PY00663B
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
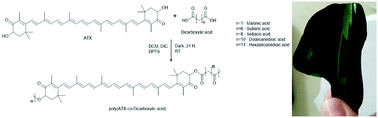
A library of novel high molecular weight polymers based on the natural carotenoid astaxanthin (ATX) has been successfully synthesized. ATX is a powerful antioxidant, known for its various therapeutic properties including anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. It is a xanthophyll with a symmetric chemical structure bearing two hydroxyl groups. Thus, its copolymerization with various diacids resulted in “polyactive” polyesters with varying chemico–physio–mechanico properties (e.g., storage moduli range: 125–1300 MPa and wetting angles of 40–110°). The potential of pATX as an antimicrobial agent was demonstrated in vitro against clinically relevant bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus MRSA252 and MSSA476; S. epidermidis 1457) showing significant reduction of both bacterial growth and biofilm formation. Lastly, we establish using pATX films in vivo had no adverse effect in direct contact with open wounds, or on the complete physiological process of whole animal wound healing.
|
Cholesterol Functionalized Aliphatic N-Substituted 8-Membere...
2018-04-10 [10.1039/C8PY00406D] |
|
Hollow polymer nanocapsules: synthesis, properties, and appl...
2018-04-10 [10.1039/C8PY00142A] |
|
Synthesis, Properties, and Crystallization of Alternating St...
2018-04-10 [10.1039/C8PY00391B] |
|
Tailored microstructure and mechanical properties of nanocom...
2018-04-09 [10.1039/C8PY00268A] |
|
Combining uretdione and disulfide reversibly degradable poly...
2018-04-09 [10.1039/C7PY01978E] |