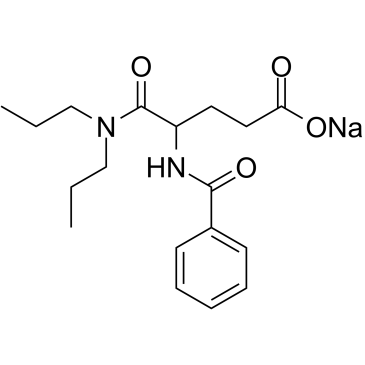
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
MA2815000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
Glutaramic acid, 4-benzamido-N,N-dipropyl-, sodium salt, dl-
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
99247-33-3
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
198806
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
7
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C18-H25-N2-O4.Na
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
356.44
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
8200 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2360 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
6110 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
8900 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2811 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
5886 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2968 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - respiratory depression Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - hematuria
-
REFERENCE :
-
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. (Oyo Yakuri Kenkyukai, CPO Box 180, Sendai 980-91, Japan) V.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 5,203,1971
|